Today, we’ll delve deep into an exciting development in the realm of decentralized hosting – running WordPress, the world’s most popular content management system (CMS), on the Akash Network. This remarkable convergence introduces a new chapter in the era of decentralized hosting, bringing along a host of advantages that redefine the norms of web hosting.
A New Era of Decentralization
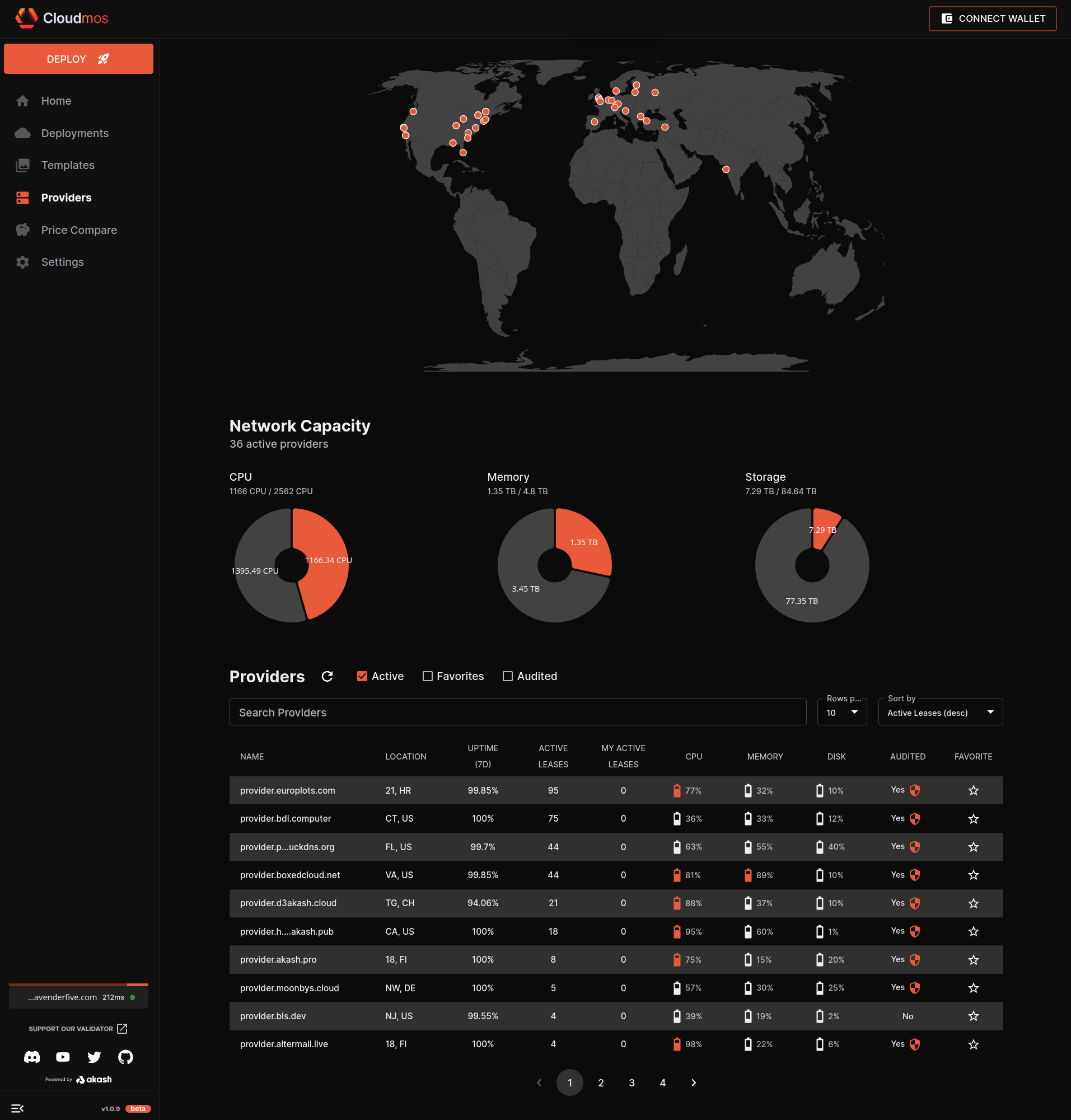
WordPress, a platform that powers more than a third of the web, now harnesses the power of Akash Network, an open-source and decentralized cloud computing platform. This new development allows WordPress to leverage underutilized compute capacity in data centers and edge servers worldwide, marking a significant milestone in decentralized hosting.
So why is WordPress on Akash such a groundbreaking leap? Here are some key reasons:
- Decentralization: Running WordPress on Akash shifts the infrastructure of your site from being reliant on a central entity to a more stable and reliable decentralized network.
- Censorship-resistant: Akash’s decentralized nature makes it resistant to censorship. It ensures your content remains accessible regardless of geopolitical constraints.
- Cost-Effective: Leveraging underused resources across various data centers, Akash often presents a more cost-effective solution than traditional hosting platforms.
- Security: Thanks to the inherent security of blockchain-based platforms, Akash ensures robust protection against a myriad of online threats.
- Flexibility: Akash provides you more control over your hosting environment and allows you to easily scale resources based on your requirements.
Delving Deeper: Advantages of WordPress on Akash Network
As we dig deeper, we uncover even more advantages of running WordPress on the Akash Network.
- Privacy and Sovereignty: With Akash, you maintain control over your data, fostering data sovereignty in contrast to traditional hosting platforms. With the rise in discussions about data privacy and security, decentralized networks like Akash offer a significant advantage. In contrast to traditional hosting platforms, where your data is stored on servers controlled by a central authority, Akash allows you to maintain control over your data. This aspect of data sovereignty is critical as it empowers the users to be in control of their own data.
- Redundancy and Resilience: The decentralized nature of Akash ensures that data and services are distributed across numerous nodes, mitigating the risk of a single point of failure and ensuring higher availability for your WordPress site. In a centralized network, if a server goes down, it can cause significant disruptions. On the other hand, in a decentralized network like Akash, data and services are distributed across numerous nodes, mitigating the risk of a single point of failure. This ensures higher availability and uptime for your WordPress site. nodes, mitigating the risk of a single point of failure and ensuring higher availability for your WordPress site.
- Scalability and Performance: Akash Network’s decentralized design also provides superior scalability and performance. Traditional web hosting services often suffer from bottlenecks during high traffic periods, causing slow loading times or even server crashes. With Akash, you can swiftly scale up resources as needed, ensuring your WordPress site remains responsive even during peak traffic.
- Innovation and Future-Proofing: By moving your WordPress site to Akash, you’re embracing an innovative, forward-thinking technology. Blockchain and decentralization are poised to be significant components of the internet’s future, known as Web 3.0. By starting now, you’re future-proofing your web presence and staying ahead of the curve.
- Customizability and Flexibility: Using Akash gives you unprecedented customizability and flexibility. The YAML configuration file you use to deploy your WordPress site allows for highly granular control over service interaction, environment variables, dependencies, and resources allocation. You have complete freedom to tweak and modify these settings to best suit your needs, something not typically available with traditional, more rigid hosting platforms.
The Bigger Picture
In addition to the benefits already discussed, here are some other broader implications of hosting WordPress on the Akash Network:
- Open Market for Compute Resources: Akash Network functions as an open marketplace for unused compute capacity, fostering a competitive market dynamic that can lead to lower costs and improved service quality.
- Enhanced Autonomy and Control: Akash grants website owners more control over their hosting environment. The YAML configuration file allows you to customize the compute resources dedicated to your WordPress site.
- Community-Driven Innovation: Being an open-source project, Akash Network enjoys the benefits of community-driven innovation, which means the technology is constantly being improved upon by a global community of developers and contributors.
- Greener Hosting: Akash Network is a more environmentally friendly choice for hosting. Unlike traditional data centers, Akash leverages underutilized compute capacity, promoting a more efficient use of existing resources.
In conclusion, running WordPress on Akash Network is about embracing a new paradigm in web hosting. It’s about taking advantage of the benefits of decentralization, from cost savings and improved performance to enhanced privacy and data sovereignty. It’s about joining an innovative community and contributing towards a more sustainable, efficient future for web hosting.
---
version: '2.0'
services:
wordpress:
image: wordpress
depends_on:
- db
expose:
- port: 80
http_options:
max_body_size: 104857600
# accept:
# - "example.com"
to:
- global: true
env:
- WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=db
- WORDPRESS_DB_USER=wordpress
- WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=testpass4you
- WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=wordpress
params:
storage:
wordpress-data:
mount: /var/www/html
readOnly: false
db:
# We use a mariadb image which supports both amd64 & arm64 architecture
image: mariadb:10.6.4
# If you really want to use MySQL, uncomment the following line
#image: mysql:8.0.27
expose:
- port: 3306
to:
- service: wordpress
- port: 33060
to:
- service: wordpress
env:
- MYSQL_RANDOM_ROOT_PASSWORD=1
- MYSQL_DATABASE=wordpress
- MYSQL_USER=wordpress
- MYSQL_PASSWORD=testpass4you
params:
storage:
wordpress-db:
mount: /var/lib/mysql
readOnly: false
profiles:
compute:
wordpress:
resources:
cpu:
units: 4
memory:
size: 4Gi
storage:
- size: 4Gi
- name: wordpress-data
size: 32Gi
attributes:
persistent: true
class: beta3
db:
resources:
cpu:
units: 1
memory:
size: 1Gi
storage:
- size: 1Gi
- name: wordpress-db
size: 8Gi
attributes:
persistent: true
class: beta3
placement:
akash:
#######################################################
#Keep this section to deploy on trusted providers
signedBy:
anyOf:
- "akash1365yvmc4s7awdyj3n2sav7xfx76adc6dnmlx63"
- "akash18qa2a2ltfyvkyj0ggj3hkvuj6twzyumuaru9s4"
#######################################################
#Remove this section to deploy on untrusted providers
#Beware* You may have deployment, security, or other issues on untrusted providers
#https://docs.akash.network/providers/akash-audited-attributes
pricing:
wordpress:
denom: uakt
amount: 10000
db:
denom: uakt
amount: 10000
deployment:
wordpress:
akash:
profile: wordpress
count: 1
db:
akash:
profile: db
count: 1